运行环境推荐
anaconda3,集成了常用的用于科学计算的包,以及对应的Python解释器(本例使用的解释器版本为3.9.12)
编辑器:VScode
摘要 本文将以迷宫探索最优路径为例,讲解A *搜索算法原理及其程序实现。
在原理讲解部分,首先从为什么要使用A *搜索算法和A *搜索算法的全局最优逻辑出发,讲解A *算法的原理。其次对A *的行动函数g(n)和启发函数h(n)的细节进行了讲解说明,并补充了启发函数的选择对于A *算法的影响。
在程序实现部分,首先从程序流程框图出发,解释A *算法的流程。其次按函数的类划分并讲解主要代码,接着展示程序的运行结果,最后对A *算法进行总结分析。
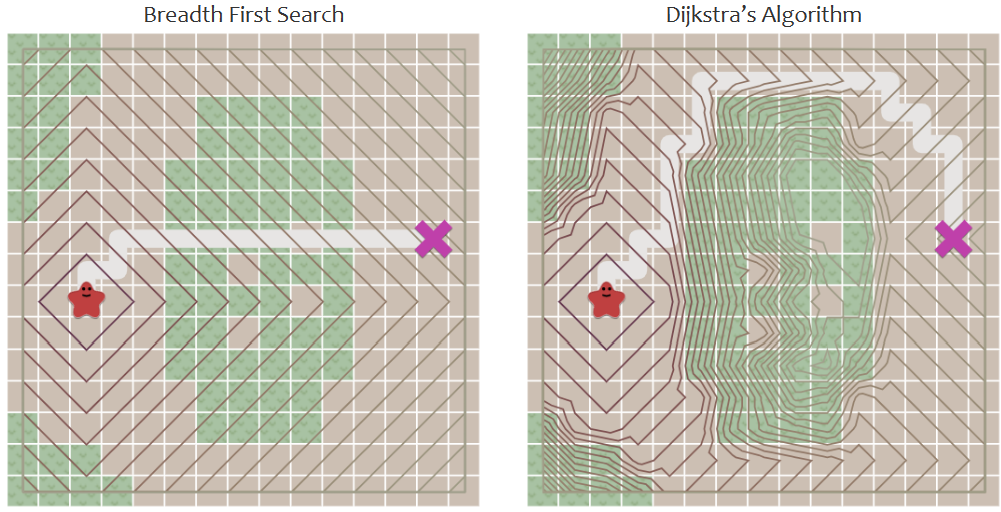
原理讲解 为什么要使用A*搜索算法? 搜索算法的核心是从起点出发,找到一条到达目标的最优(路径最短/成本最低/两者兼具)的路径。
根据不同需求,我们通常会选择:广度优先搜索(BFS)、Dijkstra算法(统一成本搜索)和贪婪优先搜索之一,下面我们逐个分析其优劣。
广度优先算法:不考虑每一步的移动成本,不断拓展边界,直到边界到达目标点,通常耗费大量时间。
Dijkstra算法:以BFS为基础,只考虑每一点的总移动成本 ,没有解决BFS耗费大量时间的问题。
贪婪优先搜索:只考虑到达终点的估计距离 ,能较快寻找到目标,但是无法保证路线全局最优。
A*搜索算法:以BSF为基础,综合考虑了总移动成本和到达终点的估计距离 ,巧妙地叠加了Dijkstra算法的成本最低和贪婪优先搜索的速度最优,具有更好的性能。
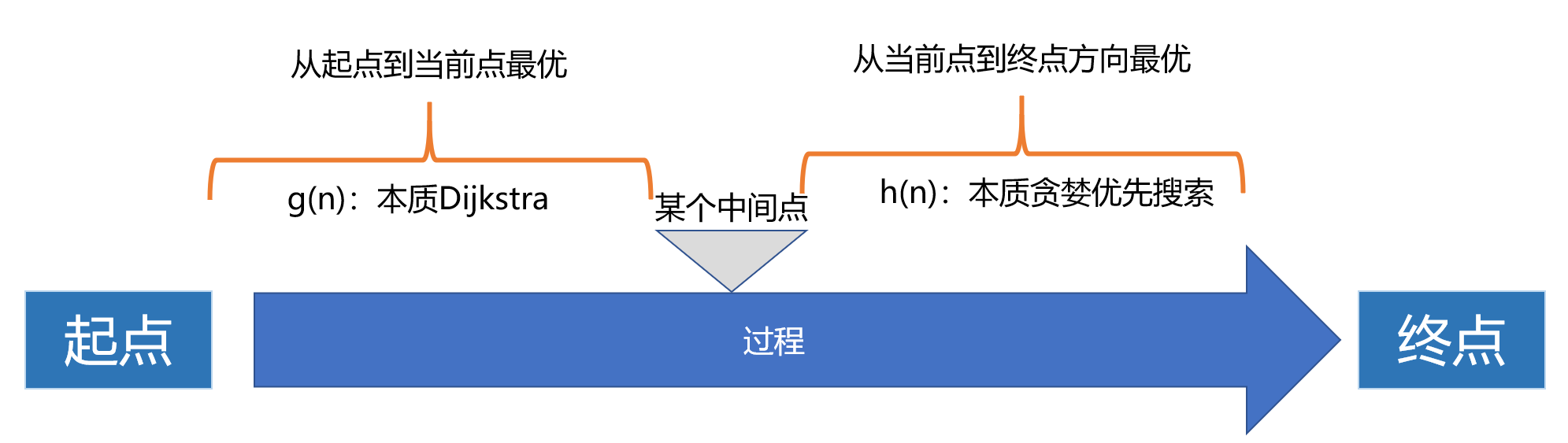
下面是A * 算法的核心公式:
说明:f(n)是总的预期成本,g(n)是当前点到起点的总移动成本,h(n)是当前点到目标点的预期代价
A *搜索算法的全局最优逻辑 首先,对于搜索算法来说,想要减少搜索的时间,那就必须要在搜索最优路径时搜索尽量少的点,最好搜索的全部节点恰好就是我们的全局最优路径。但显然,像贪婪优先搜索那样,只考虑当前点到目标点的预期距离的话,往往只能寻找到局部最优。
换句话说,贪婪优先算法只考虑单一的:当前点到目标点的估计距离,这显然不足以作为全局最优的参考指标。但是它赋予了程序有目的地前往终点方向的能力
而我们知道,BFS、Dijkstra实质上是对所有节点进行遍历,其中后者是对前者的优化,保证了起点到每一个中间点都是成本最优的选择。
那我们结合一下Dijkstra(保障当前点对起点是成本 最优的)和贪婪优先搜索(保障当前点到终点的方向 是最优的)
就可以构建一个新的参考指标:用于保证每一次从当前点选择下一个节点的时候都是全局最优的。
对行动函数 g(n) 的细节说明(可以简单理解g是小兵 ) 在A *算法中对于g(n),也就是从起点到当前点的总移动代价(沉没成本),如果我们只考虑上下左右四个方向的话,并不需要额外考虑每一步行动的代价(因为每一步都是相同的),但是如果我们从上下左右和四个边角都能被行动,那我们就需要考虑走斜边和直上直下的代价差异。
本样例中,所有的节点都是正方形,从而可知走斜边与直上直下的代价比值应为
我们为了方便计算,取1.4:1作为走斜边和直上直下的代价比值
对启发函数 h(n) 的讲解(可以简单理解h是领导 ) 在A *算法中对于h(n),也就是对当前点到目标点的预期代价估计通常采用“距离”作为度量。
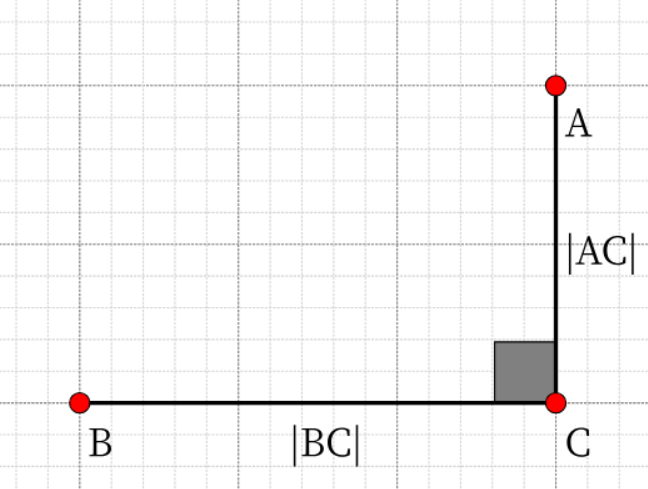
在二维地图中,我们讨论两点间距离常用的方式有两种。
曼哈顿距离
曼哈顿距离用来标明两个点在标准坐标系上的绝对轴距总和,简单来理解就是:直角三角形的两直角边之和
欧式距离
欧式距离用来标明两个点在标准坐标系上的绝对距离,简单来理解就是:直角三角形的斜边
在接下来的代码实现中,因为曼哈顿距离不需要开方,计算较为简便,因此本例选用曼哈顿距离作为启发函数的参考指标。
补充:启发函数的选择对算法的影响(了解)
情况
算法
结果
h(n)=0
A*退化为Dijkstra算法
保证能找到最短路径,但时间花费较大
h(n)=实际代价
仅拓展必要节点
时间和路径都最佳
h(n)>>g(n)
A*算法退化到贪婪优先
不保证全局路径最优,但速度很快
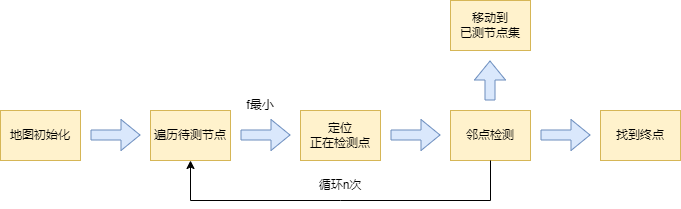
程序流程图
地图初始化:设置地图大小、起点终点、障碍物。
遍历待测节点:将起点放入待测列表(open_list)中,进而让A *算法开始运行,计算并存储列表中每一个节点的 “f(n) “ 。
定位正在检测点:查找”f(n) “最小的节点,并把它定位为正在检测的点(select_current)。
邻点检测:A *算法的核心,通过对邻点属性的判断和对预期总移动成本的权衡来选择下一个节点
移动到已测点集:将已经检测过但是没被选择的节点放入已测列表中,保证不会重复搜索
找到终点:找到终点后,由终点向起点进行最短路径的回溯,并通过调用pillow库,将结果导出为图片
AStar类 是整个算法的关键,内部包括了A *算法的初始化、最优点选择、邻点检测、节点判断和路径寻找功能的实现
初始化参数 通过构造函数,将地图属性:地图大小、起点、终点和障碍物读入,初始化 A *算法的参数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 def __init__ (self, start: Point, end: Point, map2d: Map2D ): self .path = [] self .closed_list = [] self .open_list = [] self .start = start self .end = end self .map2d = map2d
最优点选择 遍历待检测队列(open_list),找到f值最小的节点(全局最优节点),然后返回全局最优节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 def select_current (self ): min_f = sys.maxsize node_temp = None for node in self .open_list: if node.f < min_f: min_f = node.f node_temp = node return node_temp
判断节点是否在待检测队列中 通过读入要判断的节点(node),遍历open_list,判断node是否在待测队列中
1 2 def is_in_open_list (self, node ): return any ([open_node.point == node.point for open_node in self .open_list])
判断节点是否在已检测队列中 通过读入要判断的节点(node),遍历closed_list,判断node是否在已检测队列中
1 2 def is_in_closed_list (self, node ): return any ([closed_node.point == node.point for closed_node in self .closed_list])
判断节点是否是障碍物 通过读入要判断的节点(node),简单比较节点是否为”⬛”,进而判断node是否是障碍物
1 2 def is_obstacle (self, node ): return self .map2d.data[node.point.x][node.point.y] == "⬛"
相邻点检测 通过对当前节点(node)的”上下左右”和”四角”的八个方向进行检测,寻找全局最优的点,判断下一步该前往哪个节点,其中包括对邻点是否为终点、已检测点、待检测点、最优节点或障碍物的一系列判断
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 def explore_neighbors (self, node ): directions = [(1 , 0 ), (-1 , 0 ), (0 , 1 ), (0 , -1 ), (1 , 1 ), (1 , -1 ), (-1 , 1 ), (-1 , -1 )] for direction in directions: ud, rl = direction neighbor = node.get_near(ud, rl) if neighbor.point == self .end: return True if self .is_in_closed_list(neighbor) or self .is_obstacle(neighbor): continue if self .is_in_open_list(neighbor): existing_node = next (open_node for open_node in self .open_list if open_node.point == neighbor.point) if neighbor.f < existing_node.f: existing_node.father = node existing_node.g = neighbor.g else : neighbor.father = node self .open_list.append(neighbor) return False
寻找路径 这个方法将起点另外存储在回溯路径列表里(path),并不断选择最优节点前进,同时每一次前进到下一个最优节点时,都会将最优节点的父节点放进回溯路径(path)中,在最后找到终点后,利用回溯路径列表从终点回溯到起点(子节点按父节点回溯)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 def find_path (self ): start_node = AStar.Node(self .start, self .end, 0 ) self .open_list.append(start_node) while True : current_node = self .select_current() if current_node is None : return None self .open_list.remove(current_node) self .closed_list.append(current_node) if current_node.point == self .end: while current_node.father is not None : self .path.insert(0 , current_node.point) current_node = current_node.father return self .path if self .explore_neighbors(current_node): while current_node.father is not None : self .path.insert(0 , current_node.point) current_node = current_node.father return self .path
AStar.Node类 是AStar类的一个内部类,包含的初始化中间节点参数和获取相邻节点的方法是邻点检测和寻找路径的基础
初始化中间节点的参数 构造函数,初始化节点的参数:point:(当前节点的坐标)、endpoint(终点的坐标)、g(从起点到当前节点的代价),并且通过曼哈顿距离计算这条路径预计的总移动成本,是最优点选择的基础
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 def __init__ (self, point: Point, endpoint: Point, g: float ): self .point = point self .endpoint = endpoint self .father = None self .g = g self .h = (abs (endpoint.x - point.x) + abs (endpoint.y - point.y)) * 10 self .f = self .g + self .h
获取相邻节点 获取上下左右和四角共八个方向的邻点,计算并更新A *算法的g(n)值,是邻点检测的基础
ud: 上下方向的移动量(1 表示向上,-1 表示向下,0 表示不移动)
rl: 左右方向的移动量(1 表示向右,-1 表示向左,0 表示不移动)
1 2 3 4 5 6 def get_near (self, ud, rl ): near_point = Point(self .point.x + rl, self .point.y + ud) near_node = AStar.Node(near_point, self .endpoint, self .g + (10 if ud == 0 or rl == 0 else 14 )) return near_node
Map2D 类 主要是对生成的2D地图进行处理,包括地图初始化和导出地图数据的功能
初始化地图 构造函数,通过读取用户设定的地图大小,初始化地图数据,每个元素都放置一个”⬜”字符
1 2 3 4 def __init__ (self, height, width ): self .height = height self .width = width self .data = [["⬜" for _ in range (width)] for _ in range (height)]
导出地图数据 调用pillow模块,在A *算法所在的 py 文件夹内生成一个 result.png 的图片,首先将其绘制为全白色背景,再依次遍历A *算法处理后的地图数据,并在白色背景上绘制颜色,最后展示一个A *算法处理后的结果图(包含最优路径)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 def export_image (self, file_name="map.png" ): cell_size = 10 image = Image.new("RGB" , (self .width * cell_size, self .height * cell_size), "white" ) draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image) for x in range (self .height): for y in range (self .width): color = "white" if self .data[x][y] == "⬛" : color = "black" elif self .data[x][y] == "🟥" : color = "red" elif self .data[x][y] == "🟩" : color = "green" draw.rectangle([(y * cell_size, x * cell_size), ((y + 1 ) * cell_size, (x + 1 ) * cell_size)], fill=color) image.save(file_name)
设置障碍物 通过用户设置的障碍点坐标,将”⬜”(可探索位置)更新为”⬛”(障碍物)
1 2 def set_obstacle (self, x, y ): self .data[x][y] = "⬛"
设置起点和终点 通过用户设置的起点和终点坐标,将”⬜”(可探索位置)更新为”🟥”(起点或者终点)
1 2 3 def set_start_end (self, start: Point, end: Point ): self .data[start.x][start.y] = "🟥" self .data[end.x][end.y] = "🟥"
其他函数 随机放置障碍物 首先计算地图总格数,通过 obstacle_ratio 设置障碍物占全图的比例,再通过循环来实现大范围的障碍物放置,同时设置了对起点终点和现有障碍物的保护,达到增加搜索难度的目的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 total_cells = map2d.height * map2d.width obstacle_cells = int (total_cells * 0.3 ) for _ in range (obstacle_cells): x = random.randint(0 , map2d.height - 1 ) y = random.randint(0 , map2d.width - 1 ) while (x == start_point.x and y == start_point.y) or (x == end_point.x and y == end_point.y) or map2d.data[x][y] == "⬛" : x = random.randint(0 , map2d.height - 1 ) y = random.randint(0 , map2d.width - 1 ) map2d.set_obstacle(x, y)
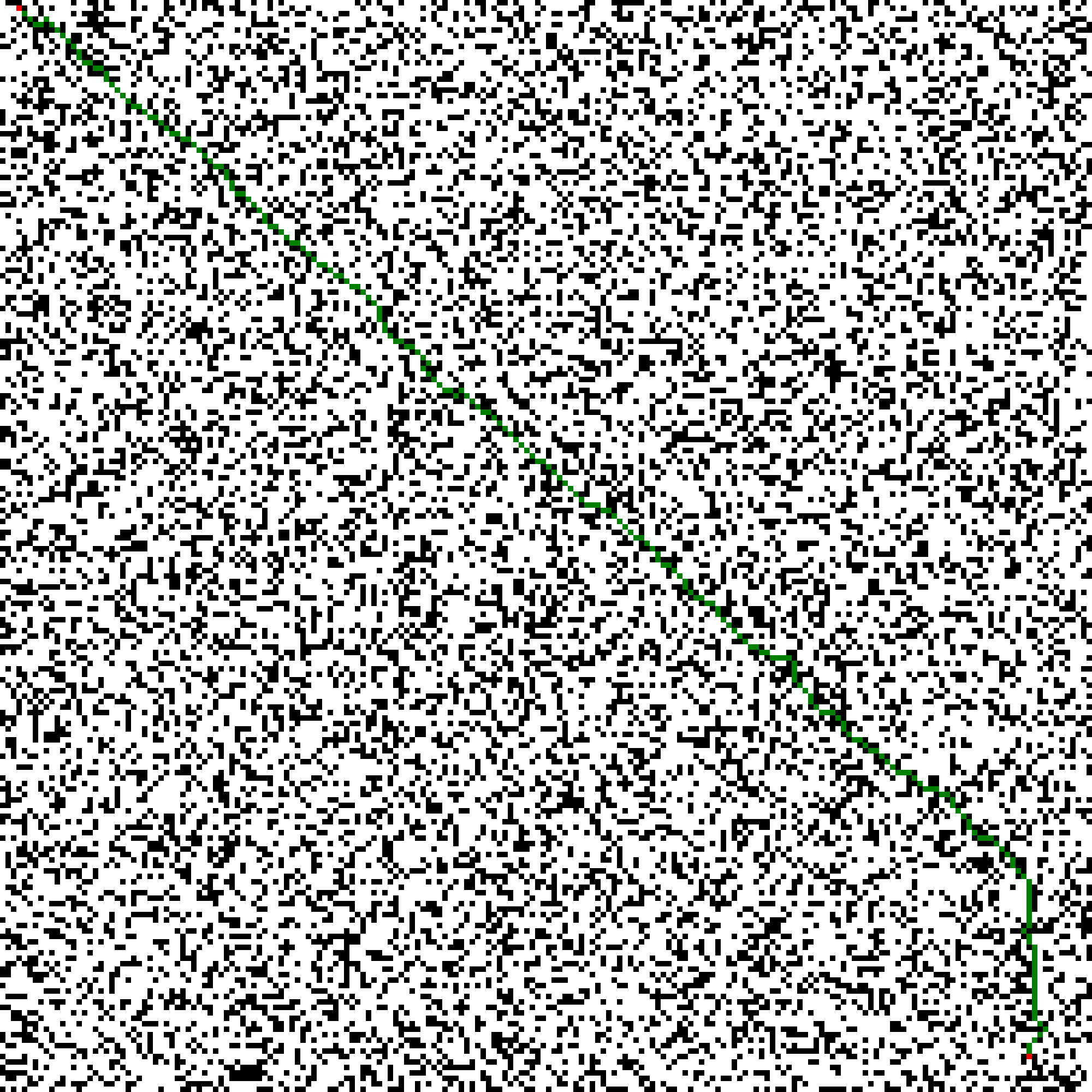
运行结果展示
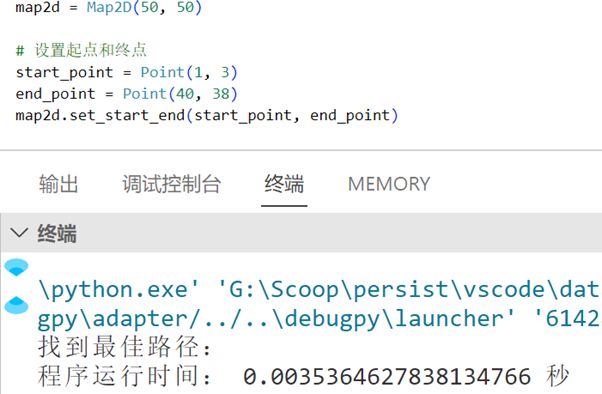
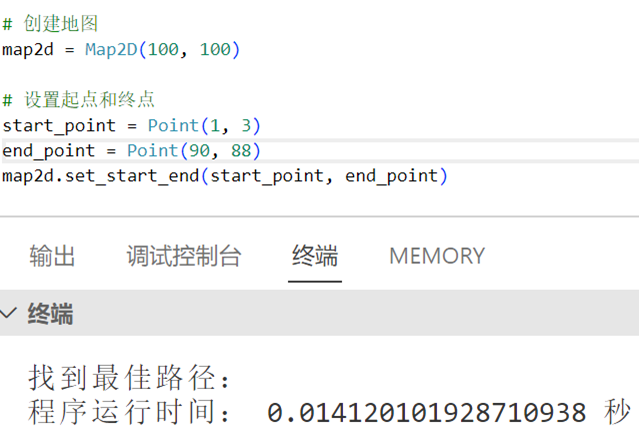
在100 x 100地图下运行
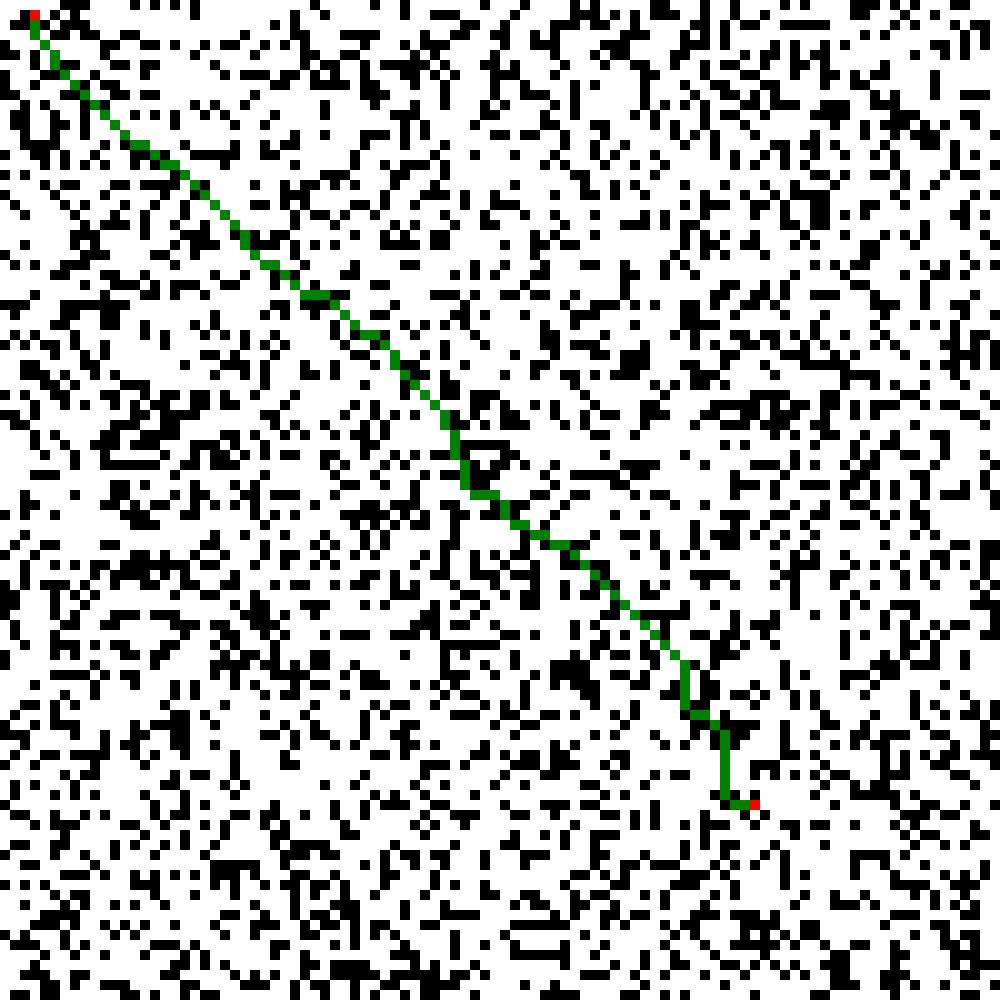
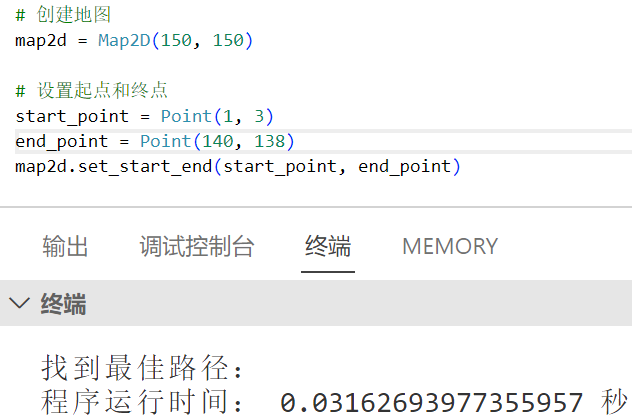
在150 x 150地图下运行
在200 x 200地图下运行
总结与分析 总体而言,A *算法在随机生成障碍物的情况下,由于其使用了启发函数,尽可能地减少了过程中不必要的搜索,所以无论是在50 x 50,100 x 100,150 x 150还是200 x 200的测试样例中均能在0.05s左右找到正确的最优路径,展现了A *算法的优越性。
附录:完整代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 import sysimport timefrom typing import List import randomfrom PIL import Image, ImageDraw""" Point类是数学坐标系的一个抽象的点,和Node类不是一回事 """ class Point : def __init__ (self, x, y )->None : self .x = x self .y = y def __eq__ (self, other )->bool : return self .x == other.x and self .y == other.y class Map2D : def __init__ (self, height, width )->None : self .height = height self .width = width self .data = [["⬜" for _ in range (width)] for _ in range (height)] def show (self, file_name="output.txt" )->None : with open (file_name, 'w' , encoding='utf-8' ) as file: for row in self .data: file.write(" " .join(row) + '\n' ) def export_image (self, file_name="map.png" )->None : cell_size = 10 image = Image.new("RGB" , (self .width * cell_size, self .height * cell_size), "white" ) draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image) for x in range (self .height): for y in range (self .width): color = "white" if self .data[x][y] == "⬛" : color = "black" elif self .data[x][y] == "🟥" : color = "red" elif self .data[x][y] == "🟩" : color = "green" draw.rectangle([(y * cell_size, x * cell_size), ((y + 1 ) * cell_size, (x + 1 ) * cell_size)], fill=color) image.save(file_name) def set_obstacle (self, x, y ): self .data[x][y] = "⬛" def set_start_end (self, start: Point, end: Point )->None : self .data[start.x][start.y] = "🟥" self .data[end.x][end.y] = "🟥" def obstacle_generate (self, ratio:int )->None : obstacle_cells = int ((self .height * self .width) * ratio) for _ in range (obstacle_cells): x = random.randint(0 , map2d.height - 1 ) y = random.randint(0 , map2d.width - 1 ) while (x == start_point.x and y == start_point.y) or (x == end_point.x and y == end_point.y) or map2d.data[x][y] == "⬛" : x = random.randint(0 , map2d.height - 1 ) y = random.randint(0 , map2d.width - 1 ) map2d.set_obstacle(x, y) """ 1.ud指的是up and down 2.rl指的是right and left """ class Node : def __init__ (self, point: Point, endpoint: Point, g: float ): self .point = point self .endpoint = endpoint self .father = None self .g = g self .h = (abs (endpoint.x - point.x) + abs (endpoint.y - point.y)) * 10 self .f = self .g + self .h def get_near (self, ud, rl ): near_point = Point(self .point.x + rl, self .point.y + ud) near_node = Node(near_point, self .endpoint, self .g + (10 if ud == 0 or rl == 0 else 14 )) return near_node class AStar : def __init__ (self, start: Point, end: Point, map2d: Map2D ): self .path = [] self .closed_list = [] self .open_list = [] self .start = start self .end = end self .map2d = map2d def select_current (self )->Node: min_f = sys.maxsize node_temp = None for node in self .open_list: if node.f < min_f: min_f = node.f node_temp = node return node_temp def is_in_open_list (self, node:Node )->bool : return any ([open_node.point == node.point for open_node in self .open_list]) def is_in_closed_list (self, node:Node )->bool : return any ([closed_node.point == node.point for closed_node in self .closed_list]) def is_obstacle (self, node:Node )->bool : return self .map2d.data[node.point.x][node.point.y] == "⬛" """ 这个函数是A*算法的核心函数,找到当前节点代价最小的邻点 用list来当作是队列的数据结构,存放探测过或者未被探测的节点,以此来进行路径探索 在路径探索中节点有三种状态 状态1.加入了队列并且已经检测了,这个单独用一个Close_list队列存放 状态2.加入了队列但是还没有检测,这个用Open_list队列存放 状态3.还没有被加入队列 """ def explore_neighbors (self, current_node:Node )->bool : up=(0 ,1 ) down=(0 ,-1 ) right=(1 ,0 ) left=(-1 ,0 ) top_right=(1 ,1 ) top_left=(-1 ,1 ) Bottom_right=(1 ,-1 ) Bottom_left=(-1 ,-1 ) directions = [up,down,right,left,top_right,top_left,Bottom_right,Bottom_left] for direction in directions: ud, rl = direction current_neighbor = current_node.get_near(ud, rl) if current_neighbor.point == self .end: return True if self .is_in_closed_list(current_neighbor) or self .is_obstacle(current_neighbor): continue if self .is_in_open_list(current_neighbor): """ 作用:在open_list中找到第一个与current_neighbor相同(坐标相同)的节点 这里有两个值得注意的点 1.在open_list中,可能有多个与current_neighbor相同(坐标相同)的节点, 出现这种情况是因为同一个节点,是可以通过多条不同的路径抵达的(意思就是g值不同) 比如说节点C是当前节点,点A与节点B都能抵达节点C且g值都相同,那么节点C此时在open_list就会被添加两次 2.previous_current_neighbor是取的在open_list中与current_neighbor相同(坐标相同)的节点中 他们唯一的区别就是g值不同但因为有多个匹配,因此这里用next函数只取一次即可 """ previous_current_neighbor = next (open_node for open_node in self .open_list if open_node.point == current_neighbor.point) """ 这时就要比较current_neighbor与previous_current_neighbor的代价了, 假如我在本次的路径探索到的current_neighbor要比我之前的路径探索到的previous_current_neighbor的代价要小 (这里时刻注意,current_neighbor与previous_current_neighbor是坐标相同的),那么我就要更新previous_current_neighbor的代价 """ if current_neighbor.f < previous_current_neighbor.f: previous_current_neighbor.father = current_node previous_current_neighbor.g = current_neighbor.g else : current_neighbor.father = current_node self .open_list.append(current_neighbor) return False def find_path (self ): start_node = Node(point=self .start, endpoint=self .end, g=0 ) self .open_list.append(start_node) while True : current_node = self .select_current() if current_node is None : return None self .open_list.remove(current_node) self .closed_list.append(current_node) if current_node.point == self .end or self .explore_neighbors(current_node): while current_node.father is not None : self .path.insert(0 , current_node.point) current_node = current_node.father return self .path if __name__ == "__main__" : map2d = Map2D(20 , 20 ) start_point = Point(1 , 3 ) end_point = Point(6 , 15 ) map2d.set_start_end(start_point, end_point) map2d.obstacle_generate(0.1 ) start_time = time.time() a_star = AStar(start_point, end_point, map2d) path = a_star.find_path() end_time = time.time() if path: print ("找到最佳路径:" ) for point in path: map2d.data[point.x][point.y] = "🟩" else : print ("未找到路径!" ) map2d.export_image("result.png" ) print ("程序运行时间:" , end_time - start_time, "秒" )